software-interview-prep
Java
Ideally, you should have one mainstream programming language down very well, to use in interviews. Java is mine.
Threads
- An interrupt is an indication to a thread that it should stop what it is doing and do something else. It’s up to the programmer to decide exactly how a thread responds to an interrupt, but it is very common for the thread to terminate.
- A thread sends an interrupt by invoking
interrupt()on theThreadobject for the thread to be interrupted. For the interrupt mechanism to work correctly, the interrupted thread must support its own interruption. - The
joinmethod allows one thread to wait for the completion of another. If it is a Thread object that is currently executing, thenthread.join();causes the current thread to pause execution until its thread terminates. - When a JVM starts up, there is usually a single non-daemon thread (which typically calls the method named
mainof some designated class). The JVM continues to execute threads until either of the following occurs:- The exit method of class
Runtimehas been called and the security manager has permitted the exit operation to take place. - All threads that are not daemon threads (
thread.setDaemon(true);wasn’t called) have died, either by returning from the call to therunmethod or by throwing an exception that propagates beyond therunmethod.
- The exit method of class
Memory
| Type | bits | Bytes |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 bit | 1 Byte |
| byte | 8 bit | 1 Byte |
| short | 16 bit | 2 Byte |
| char | 16 bit | 2 Byte |
| int | 32 bit | 4 Byte |
| float | 32 bit | 4 Byte |
| long | 64 bit | 8 Byte |
| double | 64 bit | 8 Byte |
- Memory reference (pointer): 4 Bytes.
- Object header: a few Bytes (~8 Bytes) for housekeeping info (GC, class, id, etc.).
- Array header: 12 Bytes (4 Bytes for array length).
BitSet– a bit vector with growing size, each element is a boolean with 1-bit size (not 8-bit as regular booleans).- Thread stacks are allocated outside the heap. The heap only stores objects.
- Thread stacks contain local variables (primitives, heap references) and calls to methods. Sometimes the JVM optimizes and allocates objects that never leave the stack scope on the stack (function-local objects).
- Arrays are like Objects, and are generally stored on the heap.
- Default stack size on 64-bit Linux is 256 KB for a single thread.
- Frame size for a simple method call is 32 Bytes.
- JVM Internals (read at least until Class File Structure.)
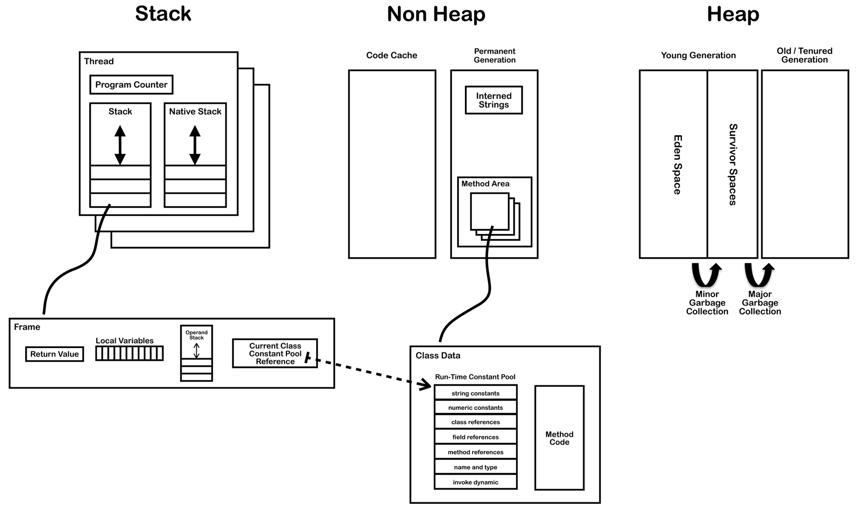
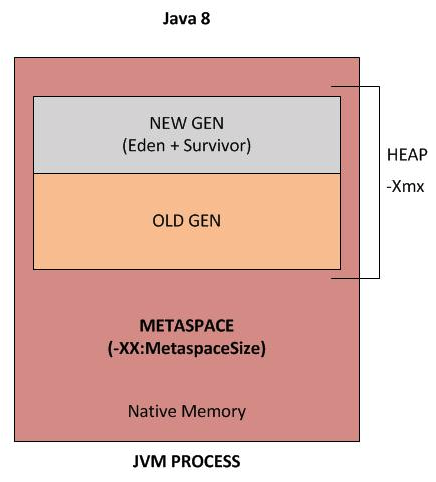
- In JDK8 8 PermGen is replaced with Metaspace, which is very similar. The main difference is that Metaspace can expand at runtime (less
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen). - If you don’t specify
MaxMetaspaceSizethe Metaspace will dynamically resize depending on the application demand at runtime. - Metaspace allocations are out of native memory.
- Metaspace garbage collection of dead classes and classloaders is triggered once the class metadata usage reaches the
MaxMetaspaceSizeoption. - Since JDK 6 interned strings are no longer allocated in the PermGen, but are instead allocated in the regular heap.
Garbage Collection
- Objects are created on the heap.
- Garbage collection is a mechanism provided by the JVM to reclaim heap space from objects eligible for GC.
- GC is done by the GC thread.
- Before removing an object from memory, GC thread invokes the
finalize()method of the object, allowing for cleanup operations (but don’t use finalizers – Effective Java 2nd Ed. Item 7). - As a developer you can’t force GC, it will only be triggered if the JVM thinks it needs to based on the Java heap size.
- You can request GC (by
Runtime.gc()orSystem.gc()) but it’s not guaranteed to happen. - If the JVM heap is full, and a new object can’t be created, an
OutOfMemoryErrorexception is thrown. - An object becomes eligible for GC if it’s not reachable from any live thread of any static reference, meaning if all its references are null.
- Cyclic dependencies aren’t references, and they will be GCed if no other objects have a reference to any of them.
- GC scenarios: all references to an object are set to null, object declared in a block and now out of scope, object is a member and the parent is eligible for GC, object in a
WeakHashMap. - Java memory leaks:
- Can be created by some hacks involving
ThreadLocal, see link - Static final fields
myString.intern()– places string in memory pool that can’t be removed- Unclosed open streams (file, network, etc.) or connections
- Native hooks that aren’t accessible to GC
- Misuse of JVM options (parameters)
HashSet/Mapwhich uses incorrecthashCode, so elements are always added
- Can be created by some hacks involving
- Available garbage collectors and how to select one.
Common JVM Options
-Xms1g– Initial heap size-Xmx2g– Hax heap size-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=200m– Add a limit to Metaspace (not limited by default)-Xmn500m– Initial and max young gen size-XX:SurvivorRatio=4– Ratio of survivor size relatively to eden size (ratio = young/survivor - 2)-Xss256k– Thread frame stack size- More options recommendations and details
Bit Arithmetics/Operations
- Can use
java.util.BitSetto work with single bits. - Positive integers are stored as simple binary numbers:
int a = 0b101;
assertEquals(5, a); // true
int zero = 0b0;
int one = 0b1;
int two = 0b10;
int three = 0b11;
int five = 0b101;
- Negative integers are stored as the two’s complement of their absolute value. The two’s complement of a positive number is, when using this notation, a negative number.
- To find the negative of a number (
x) in two’s complement:- Invert all the bits (
~x) - Add
1bit (x + 1)
- Invert all the bits (
int x = 4;
int minusX = ~x + 1;
assertEquals(-4, minusX); // true
int minusOne = 0b11111111111111111111111111111111;
int minusTwo = 0b11111111111111111111111111111110;
int minusThree = 0b11111111111111111111111111111101;
int minusFour = 0b11111111111111111111111111111100;
int minusFive = 0b11111111111111111111111111111011;
>>- Signed shift right.
- Uses the sign bit (left most bit) to fill the trailing positions after the shift.
>>>- Unsigned (logical) shift right.
- Shift right while filling zeros
0, irrespective of the sign of the number.
Primitives
intcasting drops any decimal, essentially rounding down.
Strings
- Backed by char array, can get it by calling
toCharArray(). - Strings are always immutable, and the class is
final. - Strings concatenation with the
+operator translates toStringBuilderoperations by the compiler, but creates a new instance ofStringBuilderfor every concatenation. UseStringBuilderdirectly for repeated concatenation in multiple statements with intermediate strings (single statements are fine, e.g., forString s = a + b + cuseStringBuilder).
Interning
- String literals, i.e.
String s = "hello", are interned by the compiler. - Interned strings are privately maintained in a pool, which is initially empty, by the class
String. - The
public String intern()function onStringplaces that instance in the pool and returns the canonical representation for that string object. - When the
internmethod is invoked, if the pool already contains a string equal to thisStringobject as determined by theequals(Object)method, then the string from the pool is returned. - Otherwise, this
Stringobject is added to the pool and a reference to thisStringobject is returned. - All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are interned.
==tests for reference equality (whether they are the same object)..equals()tests for value equality (whether they are logically equal).new String("test") == "test"isfalsenew String("test") == new String("test")isfalse"test" == "test"istrue- You almost always want to use
.equals(). In the rare situation where you know you’re dealing with interned strings, you can use==.
Concurrency
ITC (Inter-Thread Communication)
- Java includes an inter-process communication mechanism via the
wait(),notify(), andnotifyAll()methods. - These methods are implemented as final methods in
Object, so all classes have them. - All three methods can be called only from within a
synchronizedmethod. wait()tells the calling thread to give up the monitor and go to sleep until some other thread enters the same monitor and callsnotify().- Additional forms of
wait()exist that allow you to specify a period of time to wait. notify()wakes up the first thread that calledwait()on the same object.notifyAll()wakes up all the threads that calledwait()on the same object. The highest priority thread will run first.- You should probably not use
wait/notifydirectly and use theLockclass and others fromjava.util.concurrent.locksinstead.
Access Levels
- Having no modifier is also called package-private.
- When a class or interface is accessible to clients for each modifier:
| Modifier | Class | Package | Subclass | World |
|---|---|---|---|---|
public |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
protected |
Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| no modifier | Yes | Yes | No | No |
private |
Yes | No | No | No |
Autoboxing-Unboxing
- Autoboxing is the automatic conversion that the Java compiler makes between the primitive types and their corresponding object wrapper classes (e.g., converting an
intto anInteger). - If the conversion is the other way around (object to primitive) it’s unboxing.
- The Java compiler applies autoboxing/unboxing when a primitive/object is:
- Passed as a parameter to a method that expects an object/primitive of the corresponding wrapper/primitive type.
- Assigned to a variable of the corresponding wrapper/primitive type.
- The compiler uses
valueOfto autobox andintValueto unbox (forint, for example). - Beware of unnecessary Object creation with autoboxing/unboxing.
- Object types don’t support operators (
+for example), so using it onIntegerwill trigger unboxing and then autoboxing. - For arithmetics always prefer primitives.
- Equality checks with
==don’t unbox and so reference are compares, not values. So to compare twoIntegers use.equals()or preferrable use primitive types. - You can get
NullPointerExceptions when unboxing.